A Brief Overview of Tuberculosis
You may have heard of tuberculosis (TB) before, but do you know what it is? TB is a disease caused by bacteria that usually attacks the lungs, but it can also attack other parts of the body like the brain, spine, and kidneys. It's important to be informed about TB so you can protect yourself and others from getting sick. Read on to learn more about this disease.
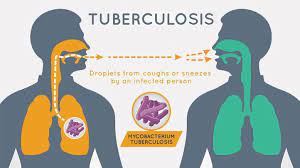
How is TB Spread?
TB is spread through the air from person to person. When an infected person coughs, sneezes, or even talks, they release tiny droplets into the air that contain the TB bacteria. People nearby can then breathe in those droplets and become infected. It's important to note that only people who are sick with TB in their lungs are able to spread the disease. People with latent TB infection (LTI) - meaning they have the TB bacteria in their bodies but are not yet sick - cannot spread the disease.
Symptoms of TB
The symptoms of TB vary depending on which part of the body is affected. However, the most common symptoms of active TB disease include:
A bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer
Pain in the chest
Coughing up blood or phlegm
Weakness or fatigue
Weight loss
No appetite
Chills
Fever
Sweating at night
Active TB disease usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body including the brain, spine, and kidneys. If you have any of these symptoms, it's important to see a doctor right away so you can get treated. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a successful outcome. People with LTI usually don't have any symptoms because their immune systems are keeping the bacteria under control. However, some people with LTI may develop active TB disease if their immune system weakens for any reason (e.g., HIV infection, cancer treatment). This is why people with LTI need to be monitored by a doctor so they can catch any signs of active TB disease early on.
Treatment for TB Disease
TB disease can be treated by taking several antibiotics for 6 to 9 months. People with TB must finish all of their antibiotics even if they start feeling better after a few weeks because if they stop taking them too soon, they may become sick again; this time, it may be harder to treat because the bacteria may be resistant to drugs. People with latent TB infection (LTI) can take 1 or 2 antibiotics for several weeks to get rid of the bacteria and prevent active TB disease from developing later on in life.
Conclusion:
Tuberculosis is a serious disease that should not be taken lightly. Although it is curable, if not treated properly, it can lead to death. Be sure to see a doctor if you think you may have contracted tuberculosis, and always finish your full course of antibiotics even if you start feeling better after a few weeks. With proper treatment, you can get rid of tuberculosis and protect yourself and others from this deadly disease.
.jpeg)



Comments
Post a Comment